This article provides a comprehensive exploration of laser ranging technology, tracing its historical evolution, elucidating its core principles, and highlighting its diverse applications. Intended for laser engineers, R&D teams, and optical academia, this piece offers a blend of historical context and modern understanding.
The Genesis and Evolution of Laser Ranging
Originating in the early 1960s, the first laser rangefinders were primarily developed for military purposes [1]. Over the years, the technology has evolved and expanded its footprint across various sectors, including construction, topography, aerospace [2], and beyond.
Laser technology is a non-contact industrial measurement technique that offers several advantages when compared to traditional contact-based ranging methods:
- Eliminates the need for physical contact with the measuring surface, preventing deformations that can lead to measurement errors.
- Minimizes wear and tear on the measurement surface since it doesn't involve physical contact during measurement.
- Suitable for use in special environments where conventional measurement tools are impractical.
Principles of Laser Ranging:
- Laser ranging utilizes three primary methods: laser pulse ranging, laser phase ranging, and laser triangulation ranging.
- Each method is associated with specific commonly used measuring ranges and levels of accuracy.
01
Laser Pulse Ranging:
Primarily employed for long-distance measurements, typically exceeding kilometer-level distances, with lower accuracy, typically at the meter level.
02
Laser Phase Ranging:
Ideal for medium- to long-distance measurements, commonly used within ranges of 50 meters to 150 meters.
03
Laser Triangulation:
Mainly used for short-distance measurements, typically within 2 meters, offering high accuracy at the micron level, although it has limited measurement distances.
Applications and Advantages
Laser ranging has found its niche in various industries:
Construction: Site measurements, topographical mapping, and structural analysis.
Automotive: Enhancing advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS).
Aerospace: Terrain mapping and obstacle detection.
Mining: Tunnel depth assessment and mineral exploration.
Forestry: Tree height calculation and forest density analysis.
Manufacturing: Precision in machinery and equipment alignment.
The technology offers several advantages over traditional methods, including non-contact measurements, reduced wear and tear, and unmatched versatility.
Lumispot Tech's solutions in the Laser Range Finding Field
Erbium-Doped Glass Laser (Er Glass Laser)
Our Erbium-Doped Glass Laser, known as the 1535nm Eye-Safe Er Glass Laser, excels in eye-safe rangefinders. It offers reliable, cost-effective performance, emitting light absorbed by the cornea and crystalline eye structures, ensuring retina safety. In laser ranging and LIDAR, especially in outdoor settings requiring long-distance light transmission, this DPSS laser is essential. Unlike past products, it eliminates eye damage and blinding hazards. Our laser uses co-doped Er: Yb phosphate glass and a semiconductor laser pump source to produce a 1.5um wavelength, making it perfect for, Ranging, and Communications.
Laser ranging, particularly Time-of-Flight (TOF) ranging, is a method used to determine the distance between a laser source and a target. This principle is widely used in various applications, from simple distance measurements to complex 3D mapping. Let's create a diagram to illustrate the TOF laser ranging principle.
The basic steps in TOF laser ranging are:
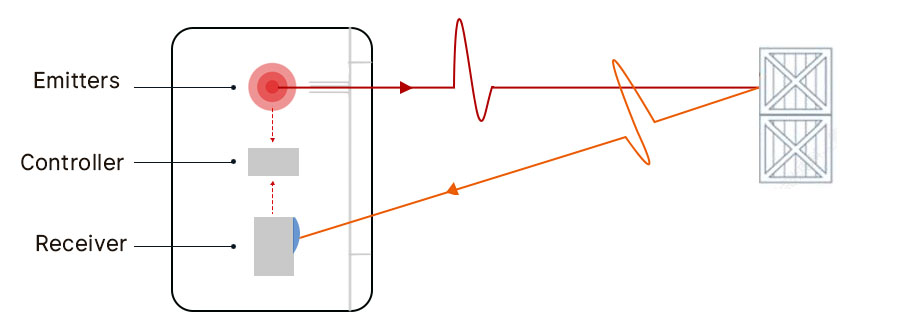
Emission of Laser Pulse: A laser device emits a short pulse of light.
Travel to Target: The laser pulse travels through the air to the target.
Reflection from Target: The pulse hits the target and is reflected back.
Return to Source: The reflected pulse travels back to the laser device.
Detection: The laser device detects the returning laser pulse.
Time Measurement: The time taken for the round trip of the pulse is measured.
Distance Calculation: The distance to the target is calculated based on the speed of light and the measured time.
This year, Lumispot Tech has launched a product perfectly suited for application in the TOF LIDAR detection field, an 8-in-1 LiDAR light source. Click to learn more if you are interested
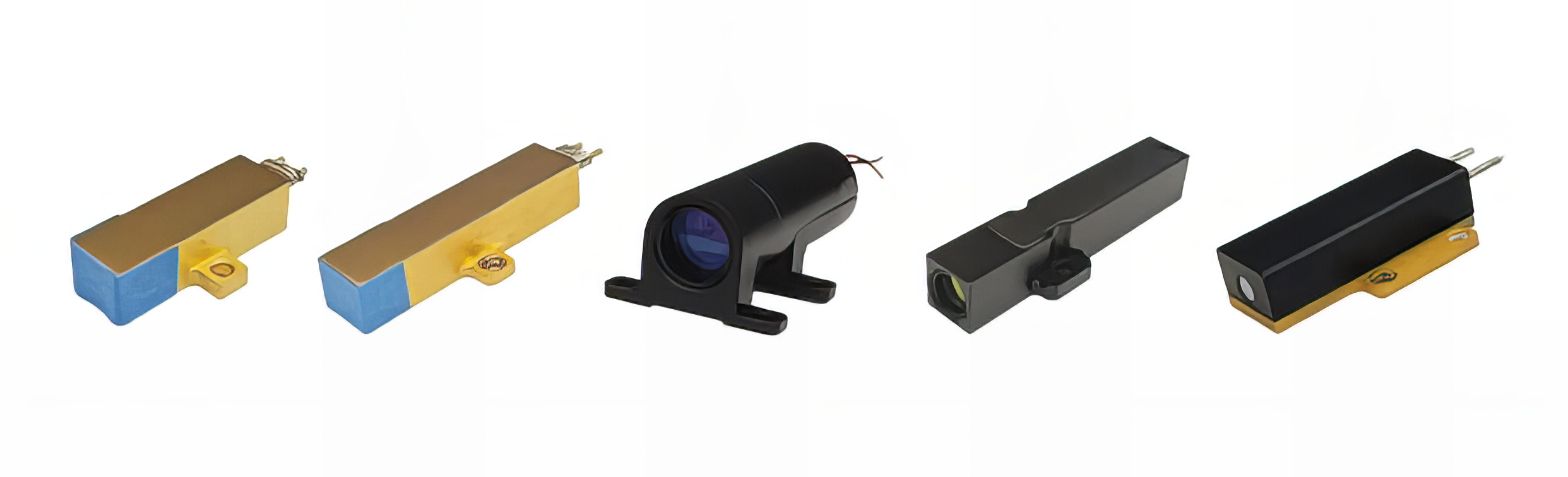
Laser Range Finder Module
This product series primarily focuses on a human eye-safe laser ranging module developed based on the 1535nm erbium-doped glass lasers and 1570nm 20km Rangefinder Module, which are categorized as Class 1 eye-safety standard products. Within this series, you'll find laser rangefinder components from 2.5km to 20km with compact size, lightweight build, exceptional anti-interference properties, and efficient mass production capabilities. They are highly versatile, finding applications in laser ranging, LIDAR technology, and communication systems.
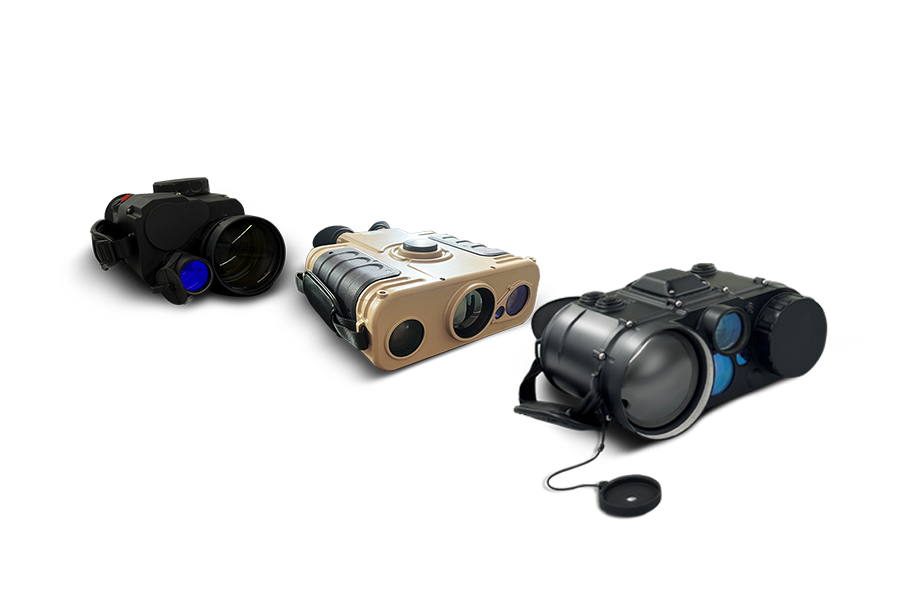
Integrated Laser Rangefinder
Military Handheld rangefinders series developed by LumiSpot Tech are efficient, user-friendly, and safe, employing eye-safe wavelengths for harmless operation. These devices offer real-time data display, power monitoring, and data transmission, encapsulating essential functions in one tool. Their ergonomic design supports both single-hand and double-hand usage, providing comfort during use. These rangefinders combine practicality and advanced technology, ensuring a straightforward, reliable measuring solution.
Why Choose Us?
Our commitment to excellence is evident in every product we offer. We understand the intricacies of the industry and have tailored our products to meet the highest standards of quality and performance. Our emphasis on customer satisfaction, combined with our technical expertise, makes us the preferred choice for professionals seeking reliable laser-ranging solutions.
Reference
- Smith, A. (1985). History of Laser Rangefinders. Journal of Optical Engineering.
- Johnson, B. (1992). Applications of Laser Ranging. Optics Today.
- Lee, C. (2001). Principles of Laser Pulse Ranging. Photonics Research.
- Kumar, R. (2003). Understanding Laser Phase Ranging. Journal of Laser Applications.
- Martinez, L. (1998). Laser Triangulation: Basics and Applications. Optical Engineering Reviews.
- Lumispot Tech. (2022). Product Catalogue. Lumispot Tech Publications.
- Zhao, Y. (2020). Future of Laser Ranging: AI Integration. Journal of Modern Optics.
Need A Free Consultation?
Consider the application, range requirements, accuracy, durability, and any additional features such as waterproofing or integration capabilities. It's also important to compare reviews and prices of different models.
[Read More: The Specific Method to select a laser rangefinder module You Need ]
Minimal maintenance is required, such as keeping the lens clean and protecting the device from impacts and extreme conditions. Regular battery replacement or charging is also necessary.
Yes, many rangefinder modules are designed to be integrated into other devices such as drones, rifles, Military Rangefinder Binoculars, etc., enhancing their functionality with precise distance measurement capabilities.
Yes, Lumispot Tech is a laser rangefinder module manufacturer, parameters can be customized as needed, or you can choose the standard parameters of our range finder module product. For more information or questions, please feel free to contact our sales team with your needs.
Most of our laser modules in the rangefinding series are designed as compact size and lightweight, especially the L905 and L1535 series, ranging from 1km to 12km. For the smallest one, we would recommend the LSP-LRS-0310F which weighs only 33g with a ranging ability of 3km.
Lasers have now emerged as pivotal tools in various sectors, particularly in security and surveillance. Their precision, controllability, and versatility make them indispensable in safeguarding our communities and infrastructure.
In this article, we will delve into the diverse applications of laser technology in the realms of security, safeguarding, monitoring, and fire prevention. This discussion aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the role of lasers in modern security systems, offering insights into both their current uses and potential future developments.
⏩ For Railway and PV inspection solutions, please click here.
Laser Applications in Security and Defense Cases
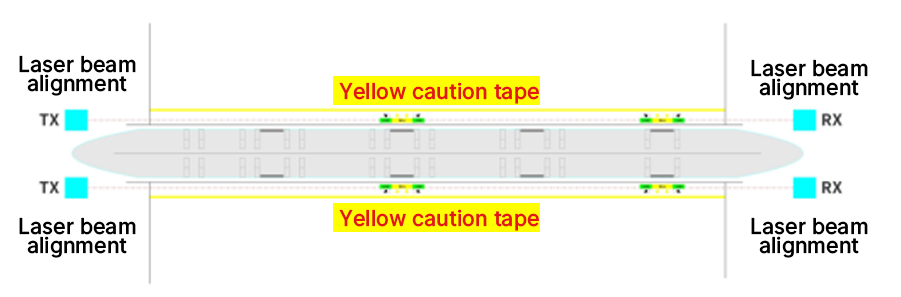
Intrusion Detection Systems
These non-contact laser scanners scan environments in two dimensions, detecting motion by measuring the time it takes for a pulsed laser beam to reflect back to its source. This technology creates a contour map of the area, allowing the system to recognize new objects in its field of view by changes in the programmed surroundings. This enables the assessment of the size, shape, and direction of moving targets, issuing alarms when necessary. (Hosmer, 2004).
⏩ Related blog:New Laser Intrusion Detection System: A Smart Step Up in Security
Surveillance Systems
In video surveillance, laser technology assists in night vision monitoring. For instance, near-infrared laser range-gated imaging can effectively suppress light backscattering, significantly enhancing the observation distance of photoelectric imaging systems in adverse weather conditions, both day and night. The system's external function buttons control gating distance, strobe width, and clear imaging, improving the surveillance range. (Wang, 2016).
Traffic Monitoring
Laser speed guns are crucial in traffic monitoring, using laser technology to measure vehicle speeds. These devices are favored by law enforcement for their precision and ability to target individual vehicles in dense traffic.
Public Space Monitoring
Laser technology is also instrumental in crowd control and monitoring in public spaces. Laser scanners and related technologies effectively oversee crowd movements, enhancing public safety.
Fire Detection Applications
In fire warning systems, laser sensors play a key role in early fire detection, quickly identifying signs of fire, such as smoke or temperature changes, to trigger timely alarms. Moreover, laser technology is invaluable in monitoring and data collection at fire scenes, providing essential information for fire control.
Special Application: UAVs and Laser Technology
The use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) in security is growing, with laser technology significantly enhancing their monitoring and security capabilities. These systems, based on new-generation Avalanche Photodiode (APD) Focal Plane Arrays (FPA) and combined with high-performance image processing, have markedly improved surveillance performance.
Green Lasers and range finder module in Defense
Among various types of lasers, green light lasers, typically operating in the 520 to 540 nanometers range, are notable for their high visibility and precision. These lasers are particularly useful in applications requiring precise marking or visualization. Additionally, laser ranging modules, which utilize the linear propagation and high accuracy of lasers, measure distances by calculating the time it takes for a laser beam to travel from the emitter to the reflector and back. This technology is crucial in measurement and positioning systems.
Evolution of Laser Technology in Security
Since its invention in the mid-20th century, laser technology has undergone significant development. Initially a scientific experimental tool, lasers have become integral in various fields, including industry, medicine, communication, and security. In the realm of security, laser applications have evolved from basic monitoring and alarm systems to sophisticated, multifunctional systems. These include intrusion detection, video surveillance, traffic monitoring, and fire warning systems.
Future Innovations in Laser Technology
The future of laser technology in security could see groundbreaking innovations, particularly with the integration of artificial intelligence (AI). AI algorithms analyzing laser scanning data could identify and predict security threats more accurately, enhancing the efficiency and response time of security systems. Moreover, as the Internet of Things (IoT) technology advances, the combination of laser technology with network-connected devices will likely lead to smarter and more automated security systems capable of real-time monitoring and response.
These innovations are expected to not only improve the performance of security systems but also transform our approach to safety and surveillance, making it more intelligent, efficient, and adaptable. As technology continues to advance, the application of lasers in security is set to expand, providing safer and more reliable environments.
References
- Hosmer, P. (2004). The use of laser scanning technology for perimeter protection. Proceedings of the 37th Annual 2003 International Carnahan Conference on Security Technology. DOI
- Wang, S., Qiu, S., Jin, W., & Wu, S. (2016). Design of A Miniature Near-infrared Laser Range-gated Real-time Video Processing System. ICMMITA-16. DOI
- Hespel, L., Rivière, N., Fracès, M., Dupouy, P., Coyac, A., Barillot, P., Fauquex, S., Plyer, A., Tauvy,
- M., Jacquart, M., Vin, I., Nascimben, E., Perez, C., Velayguet, J. P., & Gorce, D. (2017). 2D and 3D flash laser imaging for long-range surveillance in maritime border security: detection and identification for counter UAS applications. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering. DOI






-300x300.png)