1. What is the difference between pulse width (ns) and pulse width (ms)?
The difference between pulse width (ns) and pulse width (ms) is as follows: ns refers to the duration of the light pulse, ms refers to the duration of the electrical pulse during power supply.
2. Does the laser driver need to provide a short trigger pulse of 3-6ns, or can the module handle it on its own?
No external modulation module is required; as long as there is a pulse in the ms range, the module can generate an ns light pulse on its own.
3. Is it possible to extend the operating temperature range to 85°C?
The temperature range cannot reach 85°C; the maximum temperature we have tested is -40°C to 70°C.
4. Is there a cavity behind the lens filled with nitrogen or other substances to ensure that fog does not form inside at very low temperatures?
The system is designed for use at temperatures as low as -40°C and above, and the beam-expanding lens, which acts as the optical window, will not fog up. The cavity is sealed, and our products are nitrogen-filled behind the lens, ensuring the lens is within an inert gas environment, keeping the laser in a clean atmosphere.
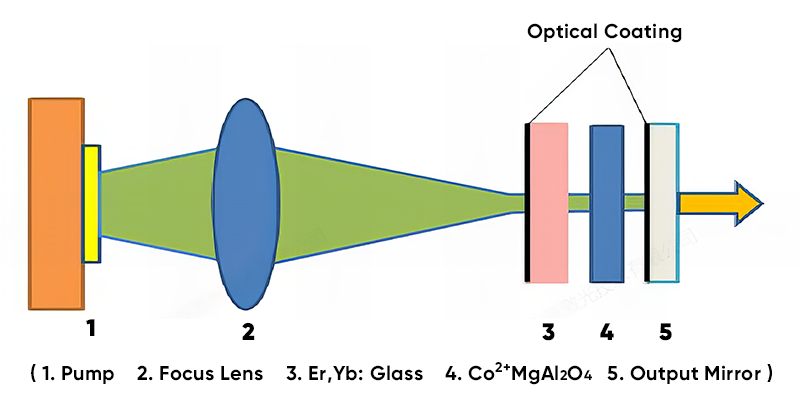
5. What’s the lasing medium?
We used Er-Yb glass as an active medium.
6. How is the lasing medium pumped?
A compact chirp on submount packed diode laser was uesd to longitudinally pump the active medium.
7. How is the laser cavity formed?
The laser cavity was formed by a coated Er-Yb glass and an output coupler.
8. How do you achieve 0.5 mrad divergency? Can you do smaller?
The incorporated beam-expansion and collimation system within the laser device is capable of constricting the divergency angle of the beam to as low as 0.5-0.6mrad.
9. Our primary concerns relate to the rise and fall times, give the extremely short laser pulse. The specification indicate a requirement of 2V/7A. Does this imply that the power supply must deliver these values within 3-6ns, or there is a charge pump integrated in the module?
The 3-6n describes the pulse duration of the laser output beam rather than the duration of the external power supply. The external power supply merely needs to gurantee:
① Input of square wave signal;
② The duration of the square wave signal is in milliseconds.
10. What are the factors affecting energy stability?
Energy stability refers to the ability of the laser to maintain consistent output beam energy over long periods of operation. The factors affecting energy stability include:
① Temperature variations
② Fluctuations in the laser power supply
③ Aging and contamination of optical components
④ Stability of the pump source
11. What is TIA?
TIA stands for “Transimpedance Amplifier,” which is an amplifier that converts current signals into voltage signals. TIA is mainly used to amplify the weak current signals generated by photodiodes for further processing and analysis. In laser systems, it is typically used together with a feedback diode to stabilize the laser output power.
12. Structure and principle of an erbium glass laser
If you are interested in our erbium glass products or would like to learn more, please feel free to contact us anytime!
Lumispot
Address: Building 4 #, No.99 Furong 3rd Road, Xishan Dist. Wuxi, 214000, China
Tel: + 86-0510 87381808.
Mobile: + 86-15072320922
Email: sales@lumispot.cn
Post time: Dec-09-2024