In the context of long-distance measurements, minimizing beam divergence is crucial. Each laser beam exhibits a specific divergence, which is the primary reason for the expansion of the beam diameter as it travels over a distance. Under ideal measurement conditions, we would expect the laser beam’s size to match the target, or even be smaller than the target size, in order to achieve the ideal state of perfect coverage of the target.
In this case, the entire beam energy of the laser rangefinder is reflected back from the target, which helps in determining the distance. In contrast, when the beam size is larger than the target, a portion of the beam’s energy is lost outside the target, resulting in weaker reflections and reduced performance. Therefore, in long-distance measurements, our main goal is to maintain the smallest possible beam divergence to maximize the amount of reflected energy received from the target.
To illustrate the effect of divergence on beam diameter, let’s consider the following example:
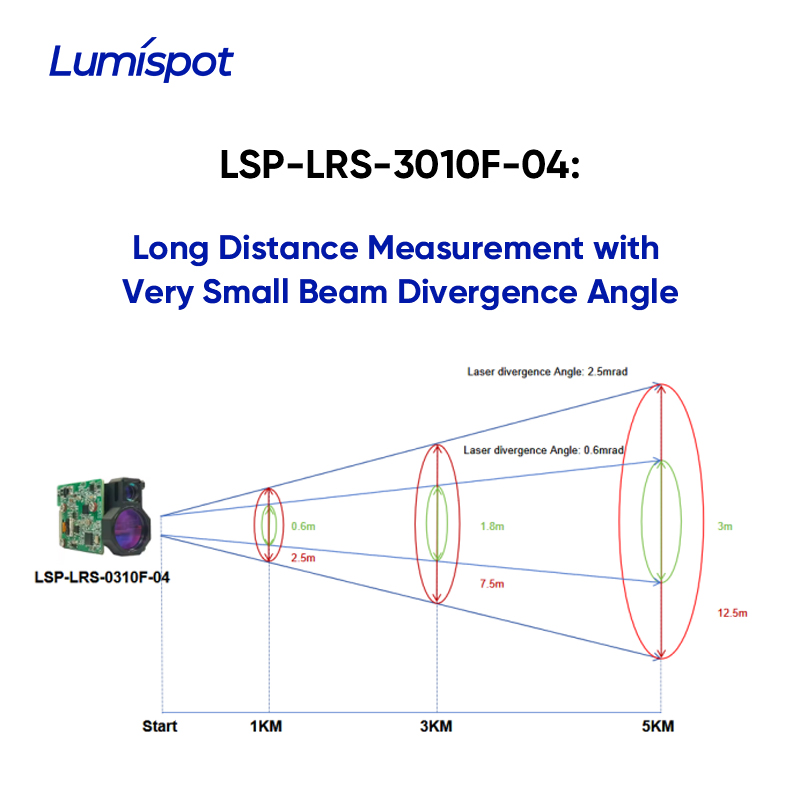
LRF with a divergence angle of 0.6 mrad:
Beam diameter @ 1 km: 0.6 m
Beam diameter @ 3 km: 1.8 m
Beam diameter @ 5 km: 3 m
LRF with a divergence angle of 2.5 mrad:
Beam diameter @ 1 km: 2.5 m
Beam diameter @ 3 km: 7.5 m
Beam diameter @ 5 km: 12.5 m
These numbers indicate that as the distance to the target increases, the difference in beam size becomes significantly larger. It is clear that beam divergence has a critical impact on the measurement range and capability. This is exactly why, for long-distance measurement applications, we use lasers with extremely small divergence angles. Therefore, we believe that divergence is a key feature that greatly affects the performance of long-distance measurements in real-world conditions.
The LSP-LRS-0310F-04 laser rangefinder is developed based on Lumispot’s self-developed 1535 nm erbium glass laser. The laser beam divergence angle of the LSP-LRS-0310F-04 can be as small as ≤0.6 mrad, enabling it to maintain excellent measurement accuracy while performing long-distance measurements. This product uses single-pulse Time-of-Flight (TOF) ranging technology, and its ranging performance is outstanding across different types of targets. For buildings, the measurement distance can easily reach 5 kilometers, while for fast-moving vehicles, stable ranging is possible at up to 3.5 kilometers. In applications such as personnel monitoring, the measurement distance for people exceeds 2 kilometers, ensuring the accuracy and real-time nature of the data.
The LSP-LRS-0310F-04 laser rangefinder supports communication with the host computer via an RS422 serial port (with custom TTL serial port service available), making data transmission more convenient and efficient.
Trivia: Beam Divergence and Beam Size
Beam divergence is a parameter that describes how the diameter of a laser beam increases as it travels away from the emitter in the laser module. We typically use milliradians (mrad) to express beam divergence. For example, if a laser rangefinder (LRF) has a beam divergence of 0.5 mrad, it means that at a distance of 1 kilometer, the beam diameter will be 0.5 meters. At a distance of 2 kilometers, the beam diameter will double to 1 meter. In contrast, if a laser rangefinder has a beam divergence of 2 mrad, then at 1 kilometer, the beam diameter will be 2 meters, and at 2 kilometers, it will be 4 meters, and so on.
If you are interested in laser rangefinder modules, feel free to contact us at any time!
Lumispot
Address: Building 4 #, No.99 Furong 3rd Road, Xishan Dist. Wuxi, 214000, China
Tel: + 86-0510 87381808.
Mobile: + 86-15072320922
Email: sales@lumispot.cn
Post time: Dec-23-2024
