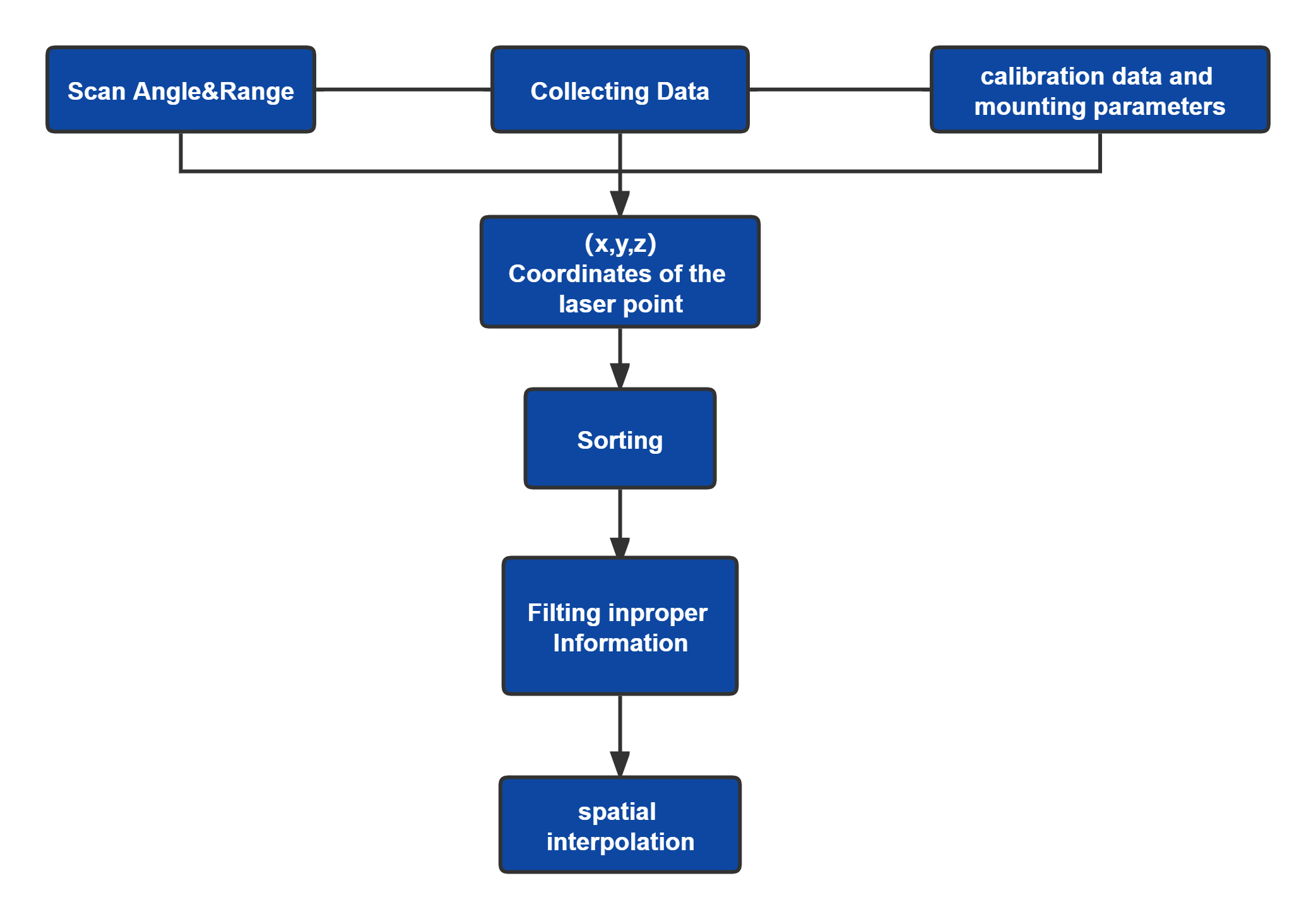
Since the late 1960s and early 1970s, most traditional aerial photography systems have been replaced by airborne and aerospace electro-optical and electronic sensor systems. While traditional aerial photography works primarily in the visible-light wavelength, modern airborne and ground-based remote sensing systems produce digital data covering the visible light, reflected infrared, thermal infrared, and microwave spectral regions. Traditional visual interpretation methods in aerial photography are still helpful. Still, remote sensing covers a wider range of applications, including additional activities such as theoretical modeling of target properties, spectral measurements of objects, and digital image analysis for information extraction.
Remote sensing, which refers to all aspects of non-contact long-range detection techniques, is a method that uses electromagnetism to detect, record and measure the characteristics of a target and the definition was first proposed in the 1950s. The field of remote sensing and mapping, it is divided into 2 sensing modes: active and passive sensing, of which Lidar sensing is active, able to use its own energy to emit light to the target and detect the light reflected from it.